프로그래머스 :완주하지 못한 선수 [3]
문제 유형 : 정렬 or 해쉬, 같은 값을 찾는 문제
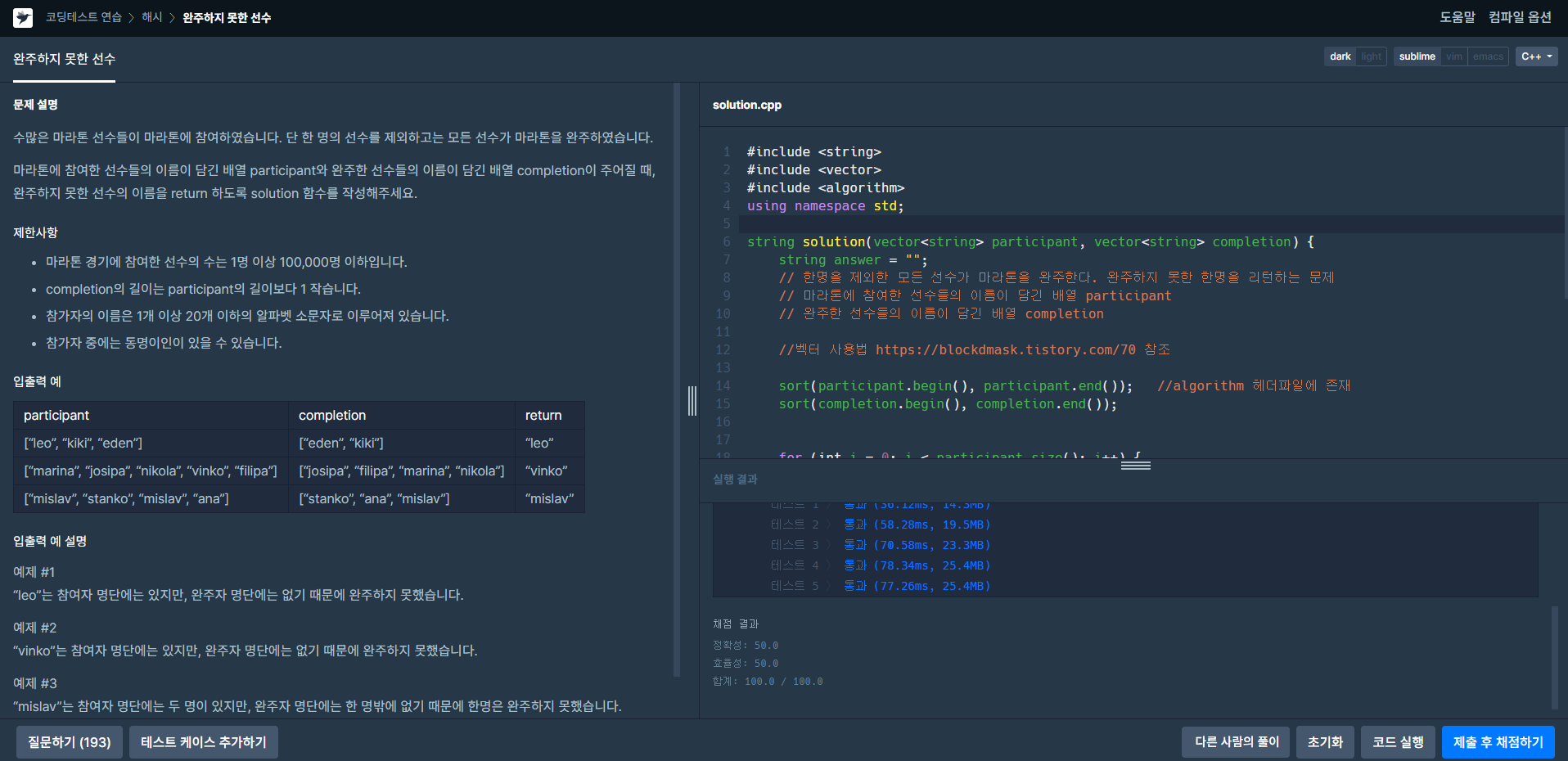
-
vector 사용법 : https://blockdmask.tistory.com/70 참조
- v.begin, v.end() : 벡터의 시작점과 끝점을 리턴, iterator와 같이 사용한다.
- v[index] : 벡터의 index에 위치한 값을 리턴, 반복자를 사용하는 것보다 빠름
-
vector의 원소 정렬
-
C++은 algorithm 라이브러리의 sort() 함수를 이용하여 벡터의 원소를 정렬할수 있다.
#include <algorithm>헤더파일을 포함시켜주어야 한다.- sort() 함수의 첫번째 두번째 매개변수는 iterator, 즉 포인터이다.
-
해결방법
-
먼저 두 벡터 안의 값을 정렬한다.
-
그리고 정렬된 두 벡터의 원소중 다른것이 있으면 그 원소가 정답이다.
ex) 정렬된 두 백터 [a,b,c] , [a,c] 가 있다면 두번째 원소가 b,c로 서로 다르고, 찾는값은 그중 b가 된다.
solution
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string solution(vector<string> participant, vector<string> completion) {
string answer = "";
// 한명을 제외한 모든 선수가 마라톤을 완주한다. 완주하지 못한 한명을 리턴하는 문제
// 마라톤에 참여한 선수들의 이름이 담긴 배열 participant
// 완주한 선수들의 이름이 담긴 배열 completion
sort(participant.begin(), participant.end()); //algorithm 헤더파일에 존재
sort(completion.begin(), completion.end());
for (int i = 0; i < participant.size(); i++) {
if (participant[i] != completion[i]) {
answer = participant[i];
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
시행착오
-> 정확성 테스트는 모두 통과했지만, 효율성 테스트에서 떨어졌다. 그 이유는 이중 for문을 사용해 시간복잡도가 O(n2)이 되기 때문이였다.
이 문제에서 요구하는 시간복잡도는 O(n)으로 시간복잡도를 줄이기 위해 정렬을 이용해 for문을 하나만 쓰도록 하는 코드로 바꾸어 효율성 테스트도 통과할수있었다.
나중에 알고보니 원래 이 문제는 해쉬를 이용해 시간복잡도를 줄이는 문제였다.
이중 for문을 쓴 코드 (효율성 text x)
vector<string>::iterator iter1 = participant.begin();
vector<string>::iterator iter2 = completion.begin();
bool isErase;
for (iter1 = participant.begin(); iter1 != participant.end(); ){
//if(iter2!=)
isErase = false;
for (iter2 = completion.begin(); iter2 != completion.end(); ++iter2) {
if (*iter1 == *iter2) {
participant.erase(iter1);
iter2 = completion.erase(iter2);
isErase = true;
break;
}
}
if (isErase == false) {
answer = *iter1;
++iter1;
break;
}
}
return answer;
