프로그래머스 :모의고사 [4]
< 프로그래머스 :모의고사>
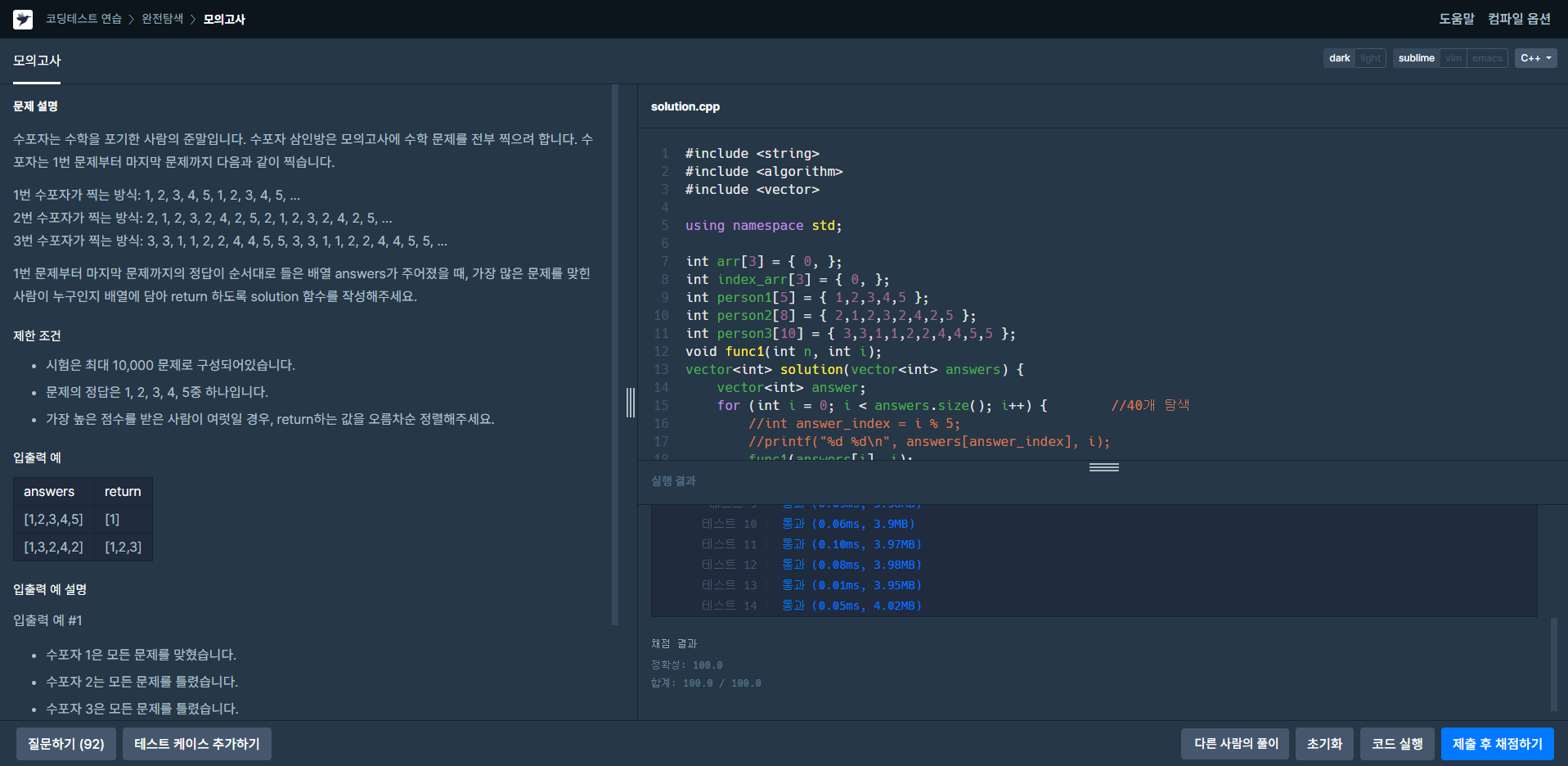
문제 유형 : 완전탐색
1번 수포자가 찍는 방식: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …
2번 수포자가 찍는 방식: 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 5, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 5, …
3번 수포자가 찍는 방식: 3, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 5, 5, 3, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 5, 5, …
로 정해져있었으므로 규칙을 찾아서 배열에 저장하였다.
int person1[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int person2[8] = { 2,1,2,3,2,4,2,5 };
int person3[10] = { 3,3,1,1,2,2,4,4,5,5 };
해결방법
test case
- answers = [1,3,2,4,2,1,3,2,4,2]
- answer = [1,2,3]
정답 배열을 돌아가면서 person…배열과 값이 같으면 +1을 해준다.
ex)
-
index가 1일때 answers[1]은 2, person1[1]= 2이므로, arr[0]의 값을 +1해준다.
-
index가 9일때 answers[9]은 2이고,
첫번째 수포자의 정답은 9%5 = 4 인 person1[4] = 5
두번째 수포자의 정답은 9%8 = 1인 person2[1] = 1
세번째 수포자의 정답은 9%10 = 9 인 person3[9] = 5 이다.
solution
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int arr[3] = { 0, };
int index_arr[3] = { 0, };
int person1[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int person2[8] = { 2,1,2,3,2,4,2,5 };
int person3[10] = { 3,3,1,1,2,2,4,4,5,5 };
void func1(int n, int i);
vector<int> solution(vector<int> answers) {
vector<int> answer;
for (int i = 0; i < answers.size(); i++) {
func1(answers[i], i);
}
int numOfElements = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
int max = *std::max_element(arr, arr + numOfElements);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (max == arr[i]) {
answer.push_back(i+1);
}
}
return answer;
}
void func1(int n,int i) { //정답과 현재 찾는 인덱스
int index = i % 5;
if (person1[index] == n) {
arr[0] += 1;
}
index = i % 8;
if (person2[index] == n) {
arr[1] += 1;
}
index = i % 10;
if (person3[index] == n) {
arr[2] += 1;
}
}
