Computer Graphics - 실습 3주차
sobel filter
- 1D 미분 필터와 blur를 주는 필터를 convolution 연산을 통해 얻은것
- 이미지의 수직, 수평 특징을 추출하는 필터이다.
sobel filter 실습
get_soble()메소드 : sobel mask 생성
def get_sobel():
derivative = np.array([[-1,0,1]])
blur = np.array([[1],[2],[1]])
x = np.dot(blur,derivative)
y = np.dot(derivative.T,blur.T)
return x,y
sobel filter main
if __name__ == '__main__':
src = cv2.imread('../image/edge_detection_img.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
dst_x = my_filtering(src, sobel_x, 'zero')
dst_y = my_filtering(src, sobel_y, 'zero')
dst = np.hypot(dst_x,dst_y)
# 0~1 사이의 값으로 변경 후 0~255로 변경
dst_x_Norm = ((dst_x - np.min(dst_x))/np.max(dst_x-np.min(dst_x))*255+0.5).astype(np.uint8)
dst_y_Norm = ((dst_y - np.min(dst_y))/np.max(dst_y-np.min(dst_y))*255+0.5).astype(np.uint8)
dst_x2 = np.sqrt(dst_x**2)
dst_y2 = np.sqrt(dst_y**2)
cv2.imshow('src', src)
cv2.imshow('dst_x ', dst_x)
cv2.imshow('dst_y ', dst_y)
cv2.imshow('dst_x2 ', dst_x2)
cv2.imshow('dst_y2 ', dst_y2)
cv2.imshow('dst_x_Norm', dst_x_Norm)
cv2.imshow('dst_y_Norm ', dst_y_Norm)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
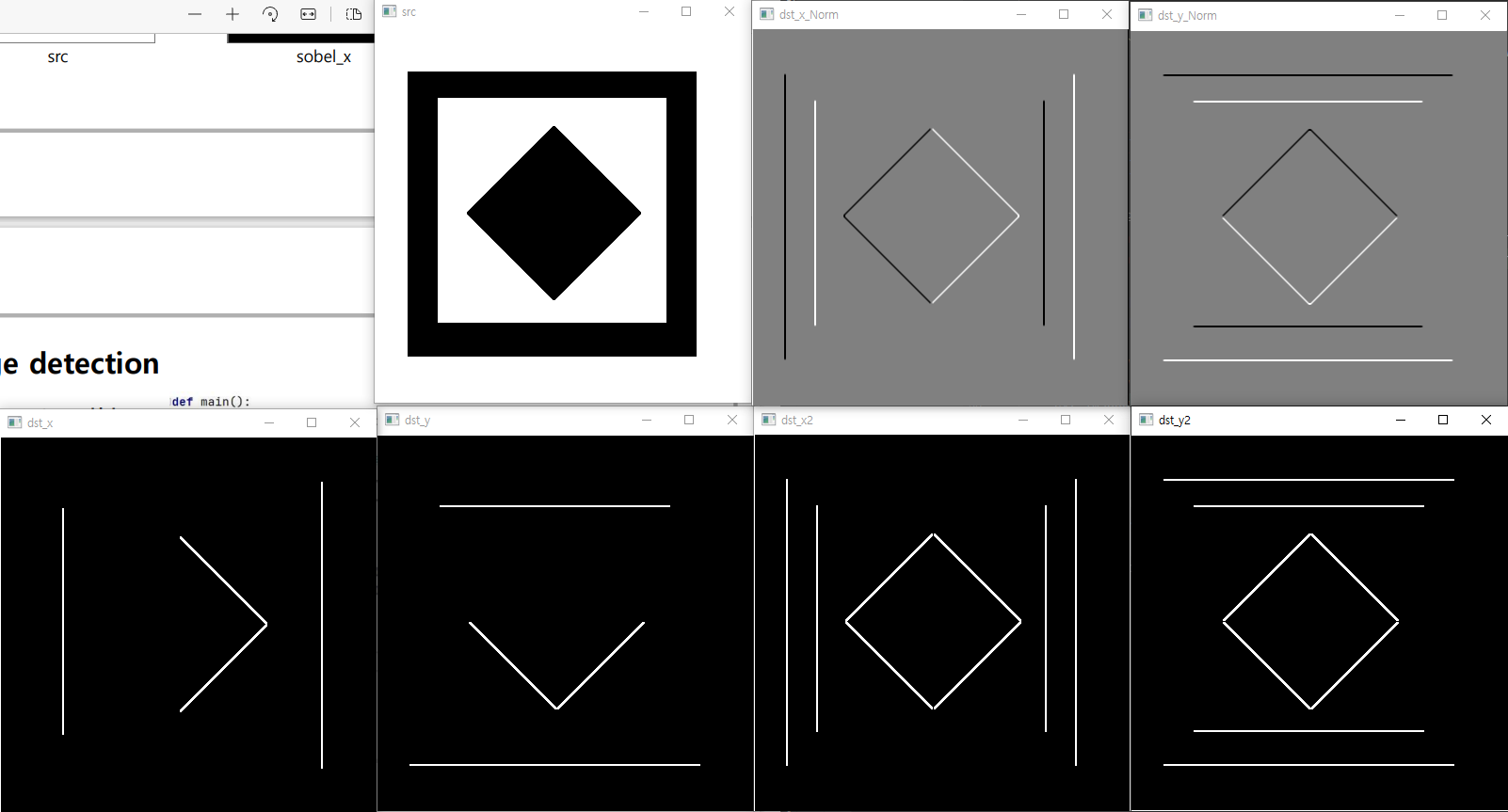
- dst_x -> dst_x_Norm
- 데이터 타입의 변화
- float -> int
- np.sqrt(sobel_x2 + sobel_y2) 이렇게 합치기!
DoG (Derivative of Gaussian)
- 가우시한 필터 후 미분 필터를 적용
- 가우시안 필터를 먼저 미분하고 연산하면 2번 필터링 할것이 1번 필터링으로 줄어든다.
수행절차

get_DoG_filter : DoG mask생성
def get_DoG_filter(fsize,sigma=1):
#TODO
#DoG mask완성
y,x = np.mgrid[-(fsize//2):(fsize//2)+1,-(fsize//2):(fsize//2)+1]
DoG_x = (-x/sigma**2) *np.exp(-((x**2 + y**2)/(2*sigma**2)))
DoG_y = (-y/sigma**2) *np.exp(-((x**2 + y**2)/(2*sigma**2)))
return DoG_x,DoG_y
DoG main
def main():
src = cv2.imread('../image/Lena.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
#DoG mask 생성.
DoG_x, DoG_y = get_DoG_filter(fsize=3,sigma=1)
dst_x = my_filtering(src, DoG_x, 'zero') # 𝐷𝑜𝐺(x) = 𝐺′(𝑥) ∗ 𝐼
dst_y = my_filtering(src, DoG_y, 'zero') # 𝐷𝑜𝐺(y) = 𝐺′(y) ∗ 𝐼
# 𝐷𝑜𝐺 𝑥 ,𝐷𝑜𝐺(𝑦)의 magnitude를 계산.
dst = np.sqrt(dst_x**2+dst_y**2)
print('dst',dst)
print('dst/255' ,dst/255)
# 0~1 사이의 값으로 변경 후 0~255로 변경
dst = ((dst - np.min(dst))/np.max(dst-np.min(dst))*255+0.5).astype(np.uint8)
print('dst',dst)
cv2.imshow('dst_x', dst_x/255)
cv2.imshow('dst_y ', dst_y/255)
cv2.imshow('dst ', dst)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
결과

결과
dst_x : 수직 특징을 추출
dst_y : 수평 특징을 추출
dst = 수평 + 수직 => dst_x + dst_y을 단순히 하면 안되고!!
거리 구하는 것 처럼 np.sqrt(dst_x**2+dst_y**2) 이런 식으로 구해야 한다.
dst = np.sqrt(dst_x**2+dst_y**2)
- dst를 이미지로 출력할때 0-1이나 0-255로 바꾸어 주어야 한다.
dst = np.sqrt(dst_x**2+dst_y**2)
print(dst)
print(dst/255)
dst = ((dst - np.min(dst))/np.max(dst-np.min(dst)) * 255+0.5).astype(np.uint8)
print(dst)
위의 결과 console
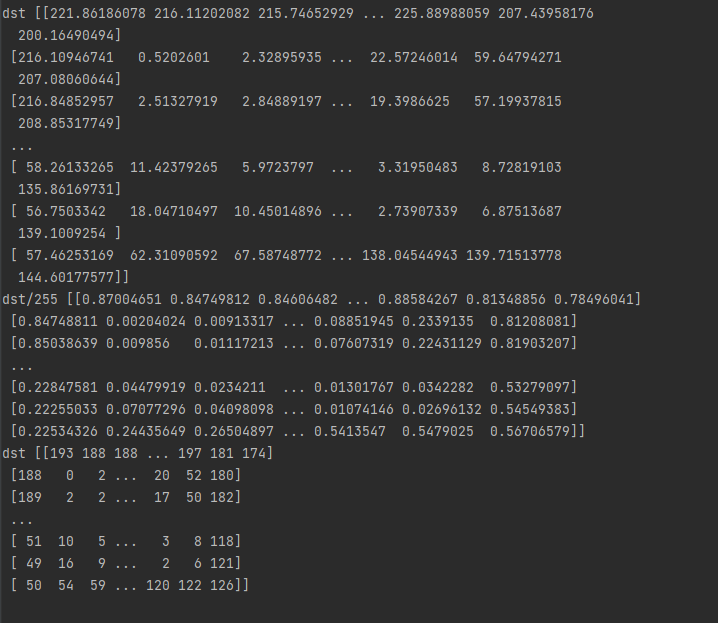
- 맨 처음은 원래 dst값 <- int도 float도 아닌값
- dst/255를 해준후에 imshow()를 해야 한다.
- 또는
dst = ((dst - np.min(dst))/np.max(dst-np.min(dst)) * 255+0.5).astype(np.uint8) - 0~1 사이의 값으로 변경 후 0~255로 변경
