Computer Graphics - 실습 4주차
Harris corner dectecion
기본원리
-
한 pixel을 중심으로 두고 작은 window를 설정, 이 window를 x축으로 u만큼, y축으로 v만큼 이동
-
그 다음 윈도우 내의 pixel값의 차이의 제곱 합을 구한다.
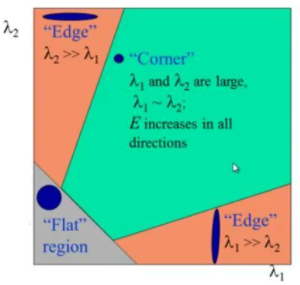
-> 얼마나 변했을 지를 계산, coner값 이라면 차이가 클 것이다!
-> E값이 크면 coner라고 판단
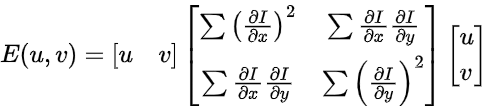
- E 값이 크려면 중간이 커야 한다. => M이라고 부르자
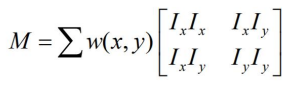
-
이 행렬 M을 고유값 분해하면 2개의 고유벡터
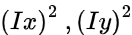 와 이에 상응하는 고유벡터를 얻을수 있다.
와 이에 상응하는 고유벡터를 얻을수 있다. -
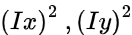 가 둘다 크면 M은 큰 값을 가지게 되고 coner라고 판단할수 있다.
가 둘다 크면 M은 큰 값을 가지게 되고 coner라고 판단할수 있다. -
둘중 하나만 큰 경우에는 edge라고 볼수있다.
Harris corner detection
- Sobel filter 적용
- 𝐼𝑥, 𝐼𝑦를 추출
-
𝐼𝑥 2 , 𝐼𝑦 2 , 𝐼𝑥𝐼𝑦 구하기
-
𝐼𝑥 2 , 𝐼𝑦 2 , 𝐼𝑥𝐼𝑦 에 Gaussian filter 적용
-
M 완성
-
det 𝑀, trace 𝑀 구하기 > 코너 판별
- 근처의 코너가 많은 경우 코너 수 줄이기
결과 코드
import cv2
import numpy as np
from library.filtering import my_filtering
def find_local_maxima(src,ksize):
(h,w) = src.shape
pad_img = np.zeros((h+ksize,w+ksize))
pad_img[ksize//2:h+ksize//2,ksize//2:w+ksize//2] = src
dst = np.zeros((h,w))
for row in range(h):
for col in range(w):
max_val = np.max(pad_img[row:row+ksize,col:col+ksize])
if max_val == 0:
continue
if src[row,col] ==max_val:
dst[row,col] = src[row,col]
return dst
def get_my_sobel():
sobel_x = np.dot(np.array([[1],[2],[1]]),np.array([[-1,0,1]]))
sobel_y = np.dot(np.array([[-1],[0],[1]]),np.array([[1,2,1]]))
return sobel_x,sobel_y
def my_get_Gaussian_filter(fshape,sigma=1):
(f_h,f_w) = fshape
y,x = np.mgrid[-(f_h//2):(f_h//2)+1,-(f_w//2):(f_w//2)+1]
filter_gaus = 1/(2*np.pi*sigma**2) * np.exp(-((x**2 + y**2 )/(2*sigma**2)))
#mask의 총 합 = 1
filter_gaus/= np.sum(filter_gaus)
return filter_gaus
def GaussianFiltering(src,fshape=(3,3),sigma=1):
gaus = my_get_Gaussian_filter(fshape,sigma)
dst = my_filtering(src,gaus)
return dst
def calc_derivatives(src):
# Todo
#3x3 sobel필터를 사용해서 Ix Iy 구하기
# : param src : 입력이미지 (흑백)
# : return : Ix,Iy
sobel_x, sobel_y = get_my_sobel()
Ix = my_filtering(src, sobel_x, 'repetition')
Iy = my_filtering(src, sobel_y, 'repetition')
return Ix,Iy
def HarrisDetector(src,gaus_filter_size=3,gaus_sigma=1,alpha=0.04,threshold_rate=0.01):
(h,w) = src.shape
#calculate Ix,Iy
Ix,Iy = calc_derivatives(src)
#Todo : IxIx,IyIy,IxIy 구하기
IxIx = np.square(Ix) # IxIx = Ix*Ix
IyIy = np.square(Iy)
IxIy = Ix*Iy
# Todo : 가우시안 필터 적용하기
G_IxIx =GaussianFiltering(IxIx,(gaus_filter_size,gaus_filter_size),gaus_sigma)
G_IyIy =GaussianFiltering(IyIy,(gaus_filter_size,gaus_filter_size),gaus_sigma)
G_IxIy =GaussianFiltering(IxIy,(gaus_filter_size,gaus_filter_size),gaus_sigma)
# Todo : har 구하기 교수님 이론 67p참고
# har = detM -a* traceM**2= g(x)g(y)-g(xy)**2
har = G_IxIx*G_IyIy - G_IxIy**2 - alpha*(G_IxIx+G_IyIy)**2 #맞나..?
# 0~1사이의 값으로 변경 후 0~255로 변경 -> 결과가 잘 나왔는지 확인하기 위해서
G_dst_har_Norm = ((har - np.min(har)) / np.max(har - np.min(har)) * 255 + 0.5).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('G_dst_har_Norm', G_dst_har_Norm)
#thresholding
har[har<threshold_rate * np.max(har)]=0
G_dst_har_thresh_Norm = ((har - np.min(har)) / np.max(har - np.min(har)) * 255 + 0.5).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('G_dst_har_thresh_Norm', G_dst_har_thresh_Norm)
dst = find_local_maxima(har,21)
return dst
def main():
src = cv2.imread('../image/zebra.png')
harris_img = src.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(src, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2GRAY).astype(np.float32)/255.
cv2.imshow('original', src)
dst = HarrisDetector(gray,gaus_filter_size=3,gaus_sigma=1,alpha=0.04)
#calculate Ix, Iy , 먼저 0-1값으로 바꿔준호 0-255의 값으로 바꾸어주었다.
# dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 3, 3, 0.04)
dst = cv2.dilate(dst, None)
interest_points = np.zeros((dst.shape[0], dst.shape[1], 3))
interest_points[dst != 0] = [0, 0, 255]
harris_img[dst != 0] = [0, 0, 255]
cv2.imshow('interest_points', interest_points)
cv2.imshow('harris_img', harris_img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
