image processing - 실습 5주차
Edge detection
sobel filter
import numpy as np
def get_sobel():
derivative = np.array([[-1,0,1]])
blur = np.array([[1],[2],[1]])
x = np.dot(blur,derivative)
y = np.dot(derivative.T,blur.T)
return x,y
def main():
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
print('sobel_x')
print(sobel_x)
print('sobel_y')
print(sobel_y)
결과
sobel_x
[[-1 0 1]
[-2 0 2]
[-1 0 1]]
sobel_y
[[-1 -2 -1]
[ 0 0 0]
[ 1 2 1]]
- sobal 실습 2
def main():
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
src = cv2.imread('../imgs/lena.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# src = src.astype(np.float32)
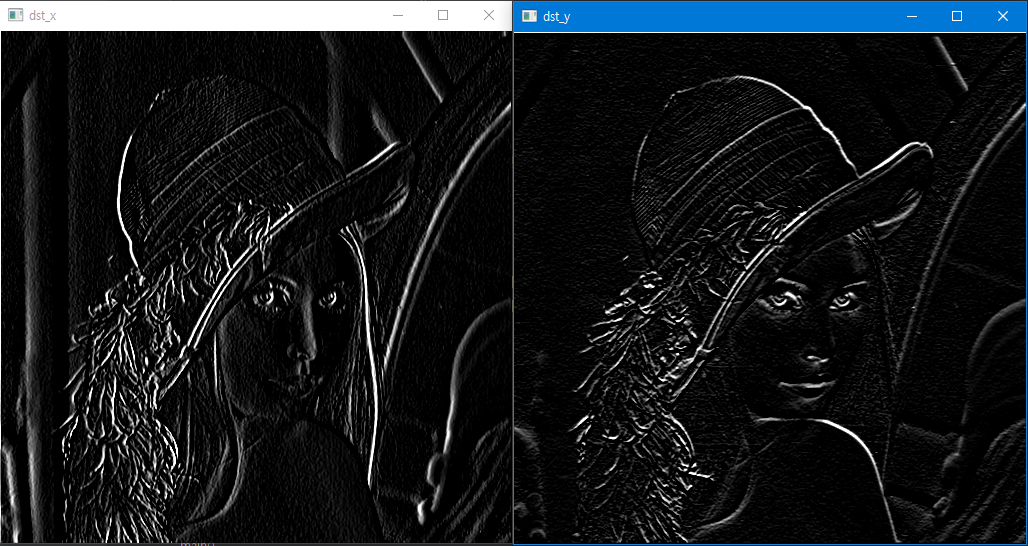
dst_x = my_filtering(src,sobel_x,'zero')
dst_y = my_filtering(src,sobel_y,'zero')
dst_x = np.clip(dst_x,0,255).astype(np.uint8)
dst_y = np.clip(dst_y,0,255).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('dst_x', dst_x)
cv2.imshow('dst_y ', dst_y)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
float와 uint의 차이
def main():
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
src = cv2.imread('../imgs/lena.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
src_float = src.astype(np.float32)
cv2.imshow('src', src)
cv2.imshow('src_float ', src_float)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
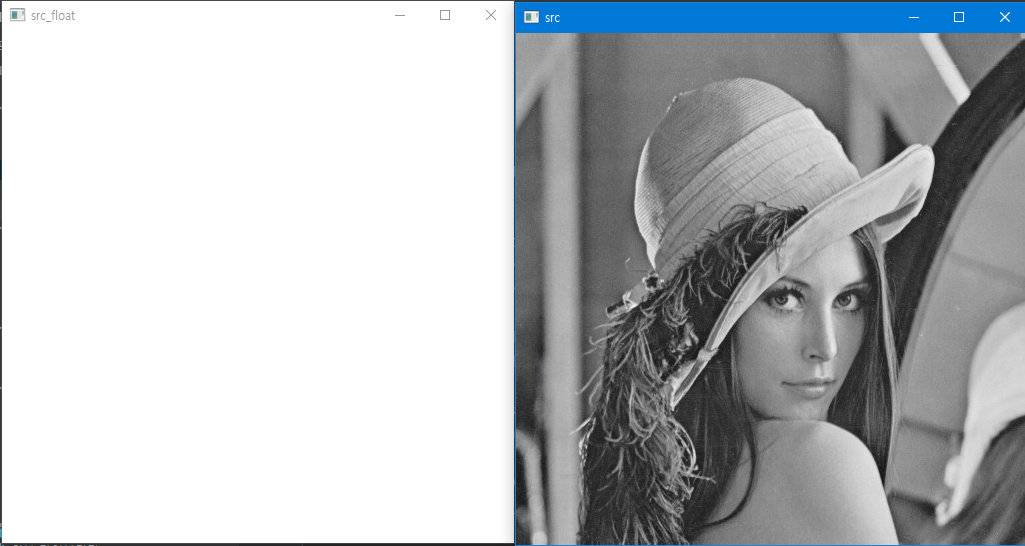
-
Data type
-
unit8 : 0 ~255
- 0 : 검정색
- 255 : 흰색
-
float : 0~1
- 0 : 검정색
-
1 : 흰색
- 1이상은 모드 1로 취급한다. 또한 0이하도 0으로 취급한다.
-
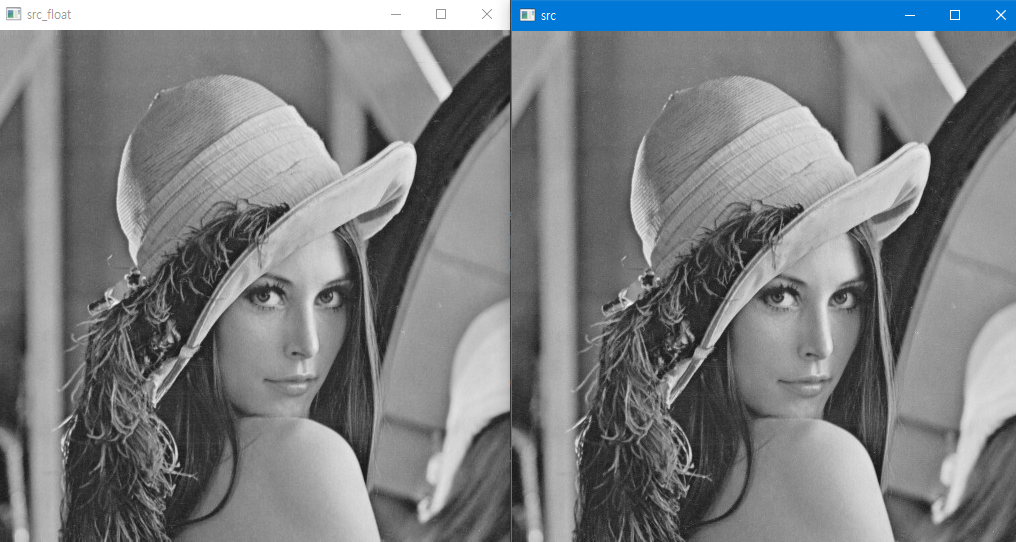
따라서 밑과 같이 코드를 바꾸면 정상적으러 사진이 출력된다.
def main():
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
src = cv2.imread('../imgs/lena.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
src_float = src.astype(np.float32)
# dst_x = my_filtering(src,sobel_x,'zero')
# dst_y = my_filtering(src,sobel_y,'zero')
# dst_x = np.clip(dst_x,0,255).astype(np.uint8)
# dst_y = np.clip(dst_y,0,255).astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow('src', src)
cv2.imshow('src_float ', src_float/255)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
sobel 실습 2
원래 이미지
def main():
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
src = cv2.imread('../imgs/edge_detection_img.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
dst_x = my_filtering(src,sobel_x,'zero')
dst_y = my_filtering(src,sobel_y,'zero')
cv2.imshow('dst_x', dst_x)
cv2.imshow('dst_y ', dst_y )
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
실행 결과
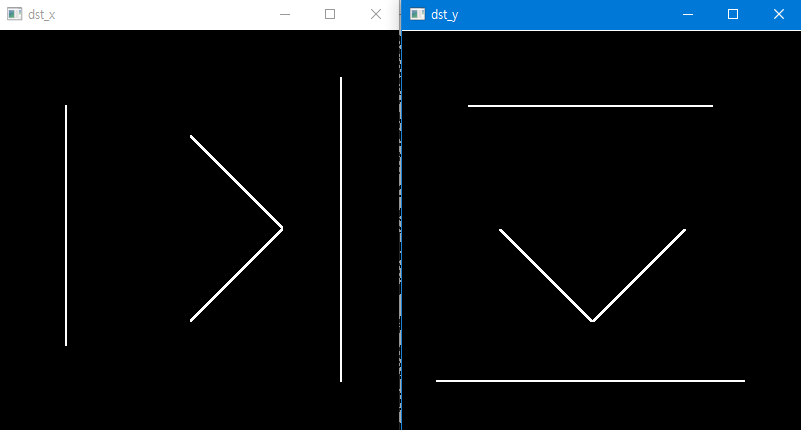
코드 수정후
def main():
sobel_x,sobel_y = get_sobel()
src = cv2.imread('../imgs/edge_detection_img.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
dst_x = my_filtering(src,sobel_x,'zero')
dst_y = my_filtering(src,sobel_y,'zero')
cv2.imshow('src', src)
----- 수정한 코드
dst_x = np.sqrt(dst_x**2)
dst_y = np.sqrt(dst_y**2)
dst_x + dst_y
-----
cv2.imshow('dst_x', dst_x)
cv2.imshow('dst_y ', dst_y )
cv2.imshow('dst_x + dst_y ', dst_x + dst_y )
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
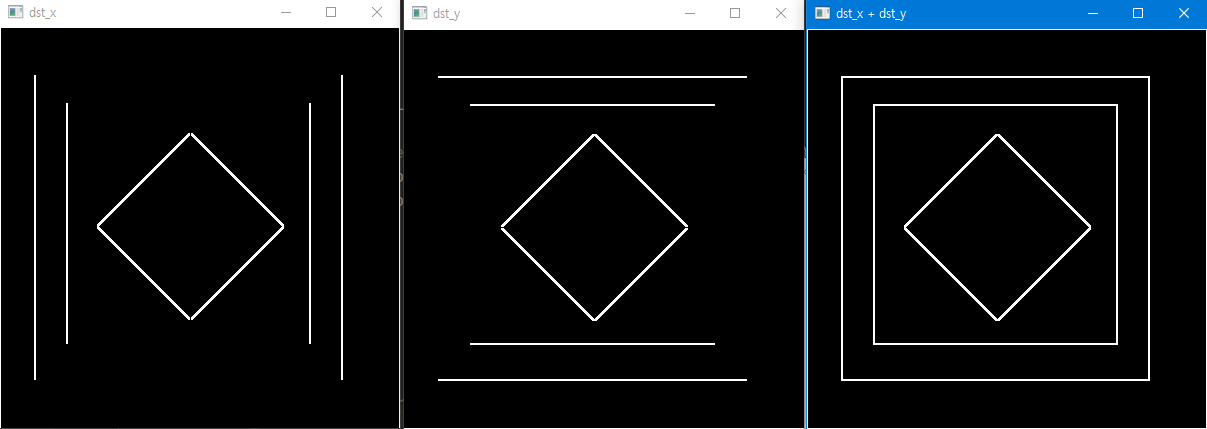
따라서 Data type이 실수일 경우
- 0보다 작은 값도 전부 0과 같은 검은색
- 1보다 큰 값도 전부 1과 같은 흰색
이라는 것을 알수있다.
threshold
-
이진화 : 영상을 흑/백으로 분류하여 처리하는 것
-
이때 기준이 되는 임계값을 threshold value라고 한다.
-
실습 코드
import numpy as np
import cv2
def main():
src = cv2.imread('../imgs/threshold_test.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
ret,dst = cv2.threshold(src,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret1,dst1 = cv2.threshold(src,0,255,cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
print('ret : ',ret)
cv2.imshow('original ', src)
cv2.imshow('threshold ', dst)
print('ret1 : ',ret1)
cv2.imshow('threshold auto ', dst1)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- 결과 화면
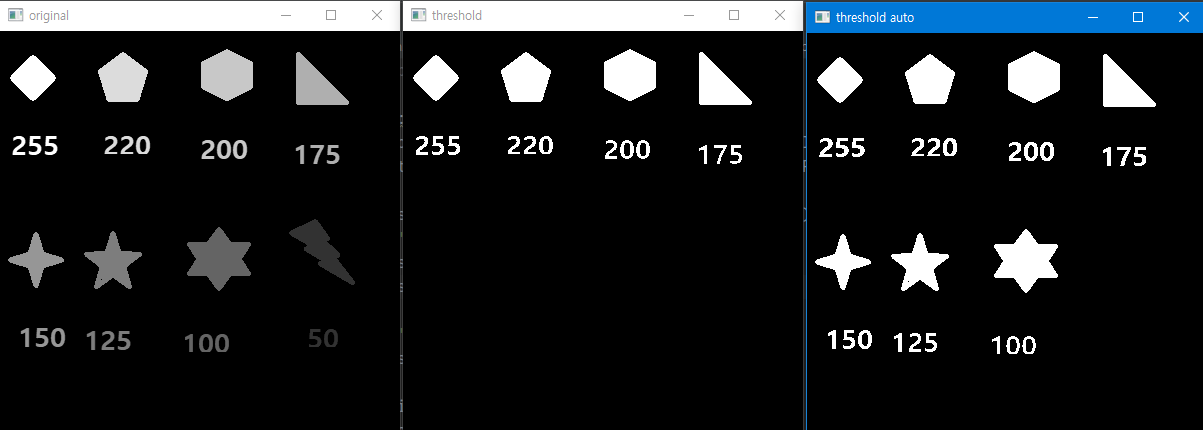
ret : 150.0
ret1 : 85.0
;lnbv
][poiuy]
