movie-app-project
결과 페이지
3.0 class component
- class 이며, react component로부터 확장된다.
- function이 아니기 때문에 return을 하지 않고, render method를 가지며, state를 사용가능하다.
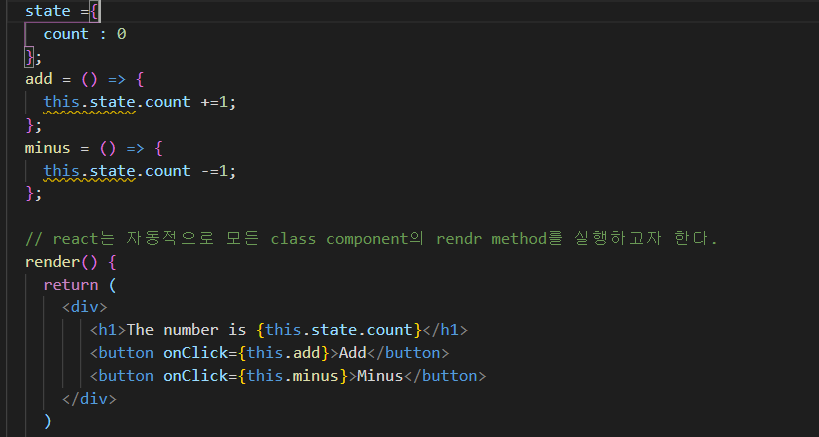
- react는 자동적으로 모든 class component의 render method를 실행한다.
state
바꾸고 싶은 data를 넣는다. object이며 component의 data를 넣을 공간이 존대한다.
- this.add()의 경우 즉시 함수를 호출하는 것이고, this.add의 경우 동작(예를 들면 클릭)할때만 호출한다는 차이가 있다.
3.1
-
이 경우 state는 바뀌지만 웹페이지에서 숫자가 바뀌지 않는다.
그 이유는 react는 render function을 refresh하지 않기 때문이다.
-
또한 console에 “Do not mutate state directly. Use setState()” == 직접 state를 변경하지 않고 setState()를 사용하라고 경고가 뜬다.
즉, 매변 state의 상태를 변경할 때 react가 render function을 호출해 refresh해주어야 한다.
-> setState function을 호출하면, refresh를 할수있다.
-
setState
state는 object이다. 따라서 setState는 새로운 state를 받아야 한다.
따라서 this.state.count = 1 이 아니라 setState({count:1})을 사용해야 한다. (아래와 같이)

setState를 호출하면, react는 state를 refresh하고 render function을 호출할 것 이다.!!!!
참고
-
this.setState({ count: this.state.count - 1 });
-
this.setState((current) => ({ count: current.count + 1 }))
1의 방식보다 2의 방식이 더 좋은 방식이다.
- 1의 방식은 수행동안 this.state.count가 업데이트 되어서 이상한 결과가 생성될 수도 있지만
-
2의 방식은 항상 ‘current’한 상태를 얻을수있기 때문이다.
- (setState는 비동기로 처리되어 여러번 호출되면 처리순서가 바뀔수있다.)
life cycle method : 리액트가 component를 생성하고, 없애는 방법
-
mounthig
constructor(): 시작하기 전- getDerivedStateFromProps()
render()componentDidMount(): component가 처음으로 render됬다는것을 알려준다.
의 순서로 실행된다.

-
updating
- getDerivedStateFromProps()
- shouldComponentUpdate() : 기본적으로 업데이트를 할지 말지에 대한것
render(): setState를 실행할때마다 실행된다.- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
componentDidUpdate()-> console.log(‘l just updated’);

-
unmouthing : component가 죽을때
componentWillUnmount()
결론
※ Mounting- component의 태어남
▶ constructor() -JS에서 class를 만들 때 호출되는 것 -coponent가 mount될 때 호출됨 ▶ componentDidMount()-component가 처음 render될 때 호출됨
※ Updating ▶ componentDidUpdate()-coponet가 업데이트될 때 호출됨
※ Unmounting- coponent가 죽는 것 ▶ componentWillUnmount()
setState()호출=>component 호출=>render 호출 =>업데이트 완료 후 coponentDidUpdate 실행
3.3
-
이전 문법
class App extends React.Component { state = { isLoding:true }; render() { return <div>{this.state.isLoding ? "Loding" : "We are ready"}</div> } } -
es6 사용
class App extends React.Component { state = { isLoding:true }; render() { const {isLoding} = this.state; return <div>{isLoding ? "Loding" : "We are ready"}</div> } } -
render을 하면 가장 처음 호출되는 LifeCycle : ComponentDidMount()
4.1

const {data: {data :{movies}}} =await axios.get("https://yts proxy.nomadcoders1.now.sh/list_movies.json");
console.log(movies);
이와 같이 es6의문법을 사용하면 간편하다.
- axios, asyns사용 :비동기 처리로 axios.get을 기다린다.
// async, 비동기로 처리함으로써 axios를 다 get할때까지 기다리도록 한다.
getMovies = async() => {
// getMovies는 axios.get을 사용한다. 하지만 axios.get은 완료되기까지 시간이 걸리기 때문에 await를 넣었다.
const {data: {data :{movies}}} =await axios.get("https://yts-proxy.nomadcoders1.now.sh/list_movies.json");
this.setState({movies, isLoding:false}) // isLoding을 false로 설정해, movies의 로딩이 끝나면 Loading을 바뀌게 한다.
}
4.3
const todoItems = todos.map((todo, index) =>
// Only do this if items have no stable IDs <li key={index}> {todo.text}
</li>
);
rendering한 항목에 대해 안정적인 id가 없는 경우, map함수의 index를 사용할수 있다.
(단, 항목의 순서가 바뀔 수 있는 경우 key에 인덱스를 사용하는 것은 권장하지 않는다. )
